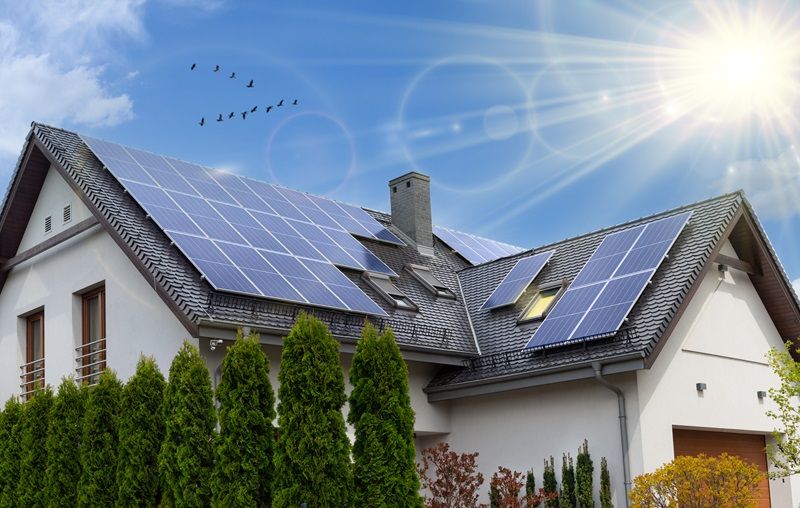
What is Net Metering?
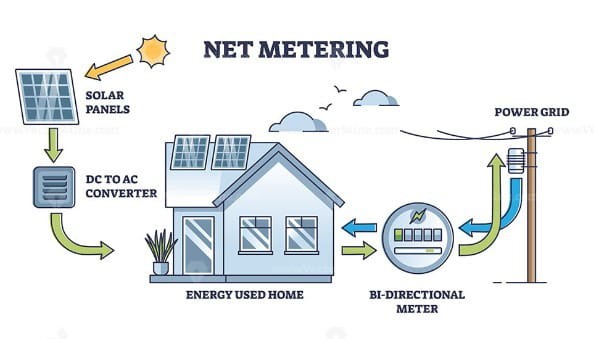
Net metering is a billing arrangement that allows solar system owners to connect their photovoltaic (PV) systems to the electric grid. Under this arrangement, any excess electricity generated by the solar system is fed back into the grid, and the owner receives credits for the surplus energy. These credits can then be used to offset the energy consumed by the grid when the solar system is not producing sufficient electricity, such as during nighttime or cloudy days.
Benefits of Net Metering Solar
Here are 4 important benefits of net metering solar:
• Renewable Energy Promotion
Net metering encourages the widespread adoption of renewable energy sources, particularly solar power. By incentivizing individuals and businesses to install solar panels, net metering helps increase the overall share of clean energy in the electricity grid. This promotes sustainability, reduces greenhouse gas emissions, and mitigates climate change.
• Grid Support and Stability
Solar systems connected through net meter contribute to the stability and reliability of the electricity grid. During times of high solar energy production, excess electricity is fed back into the grid, reducing the strain on traditional power plants. This distributed generation approach helps to meet energy demands and minimizes the need for costly grid infrastructure upgrades.
• Financial Savings
Net metering allows solar system owners to offset their electricity bills by generating excess energy and feeding it back into the grid. By receiving credits for the surplus electricity produced, they can significantly reduce their overall energy costs. This can lead to substantial savings on monthly utility bills, making solar power a financially viable investment.
• Local Job Creation and Economic Growth
The adoption of net metering and solar power systems stimulates local job creation and economic growth. The installation, maintenance, and monitoring of solar systems require skilled professionals, fostering employment opportunities within the renewable energy sector. Furthermore, the growth of the solar industry can attract investments, drive innovation, and contribute to a sustainable economy.
How does net metering work?
Say you’ve installed a solar panel system and you live in an area with a net metering program. When your photovoltaic system produces more electricity than you’re using at any point during the day, the electricity is sent back to the grid, running your electric meter in reverse.
When your energy use is higher than your solar panel production, either at night or on cloudy days, you’ll pull electricity back from the grid, running your meter forward. At the end of the month or year, you’ll be billed the net amount of what you send to the grid and what you pull from the grid: hence “net metering”.
With a correctly sized solar energy system, you can produce enough electricity to match your home’s electricity use for the entire year. However, the amount of electricity your solar panels produce will vary throughout the year––more in sunnier summer months and less when the sun is lower in the sky and sets earlier in the winter. Net metering helps you to account for these seasonal differences in solar production by crediting you for the excess electricity your panels produce so that you can use it at a later date.
Read More-Why Monsoon is the Right Time to Install Solar
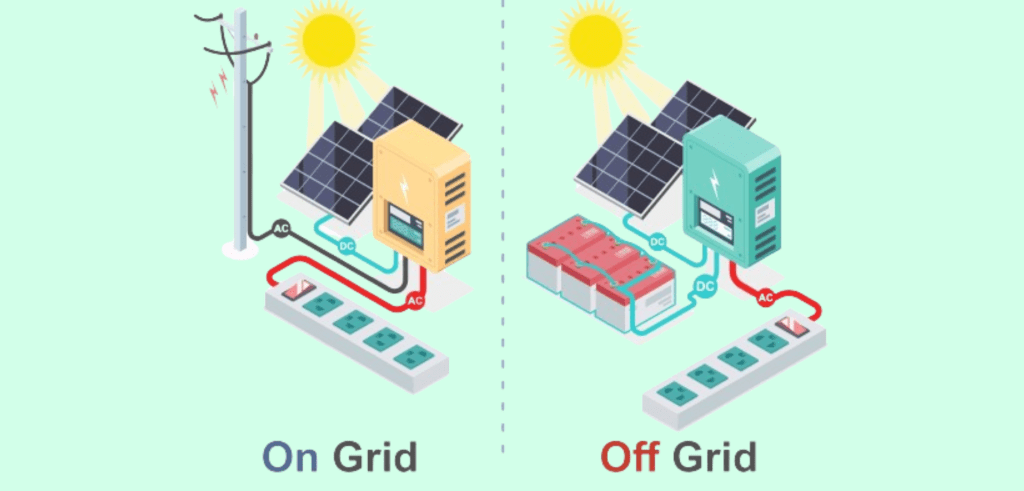
Read More-Differences Between On-Grid and Off-Grid Solar System